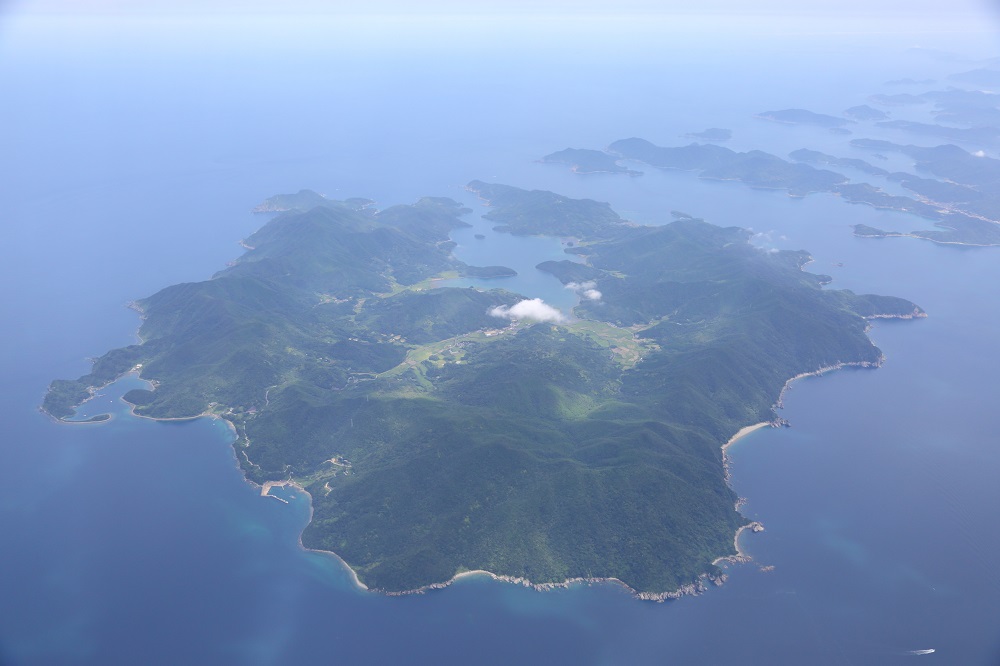
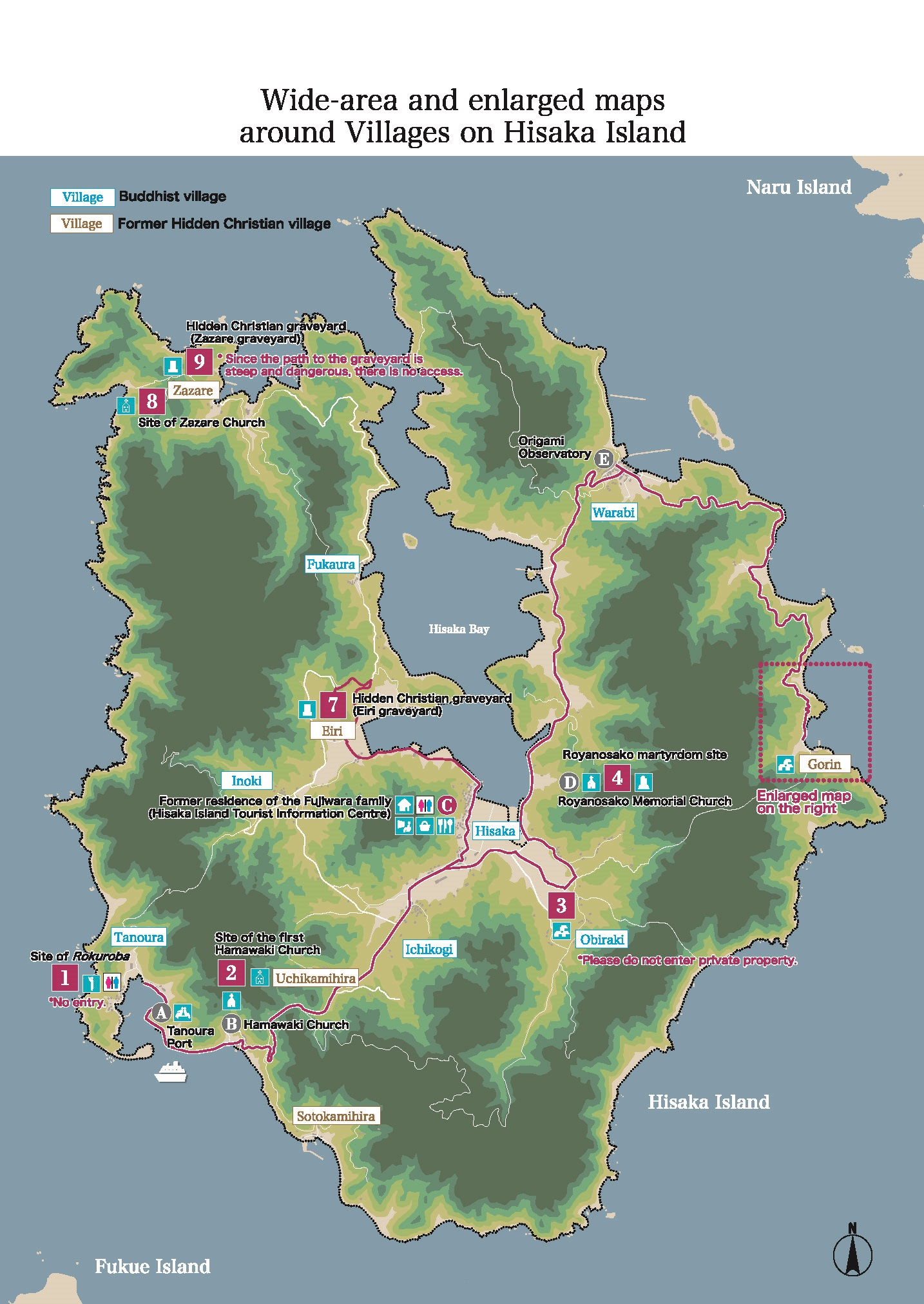
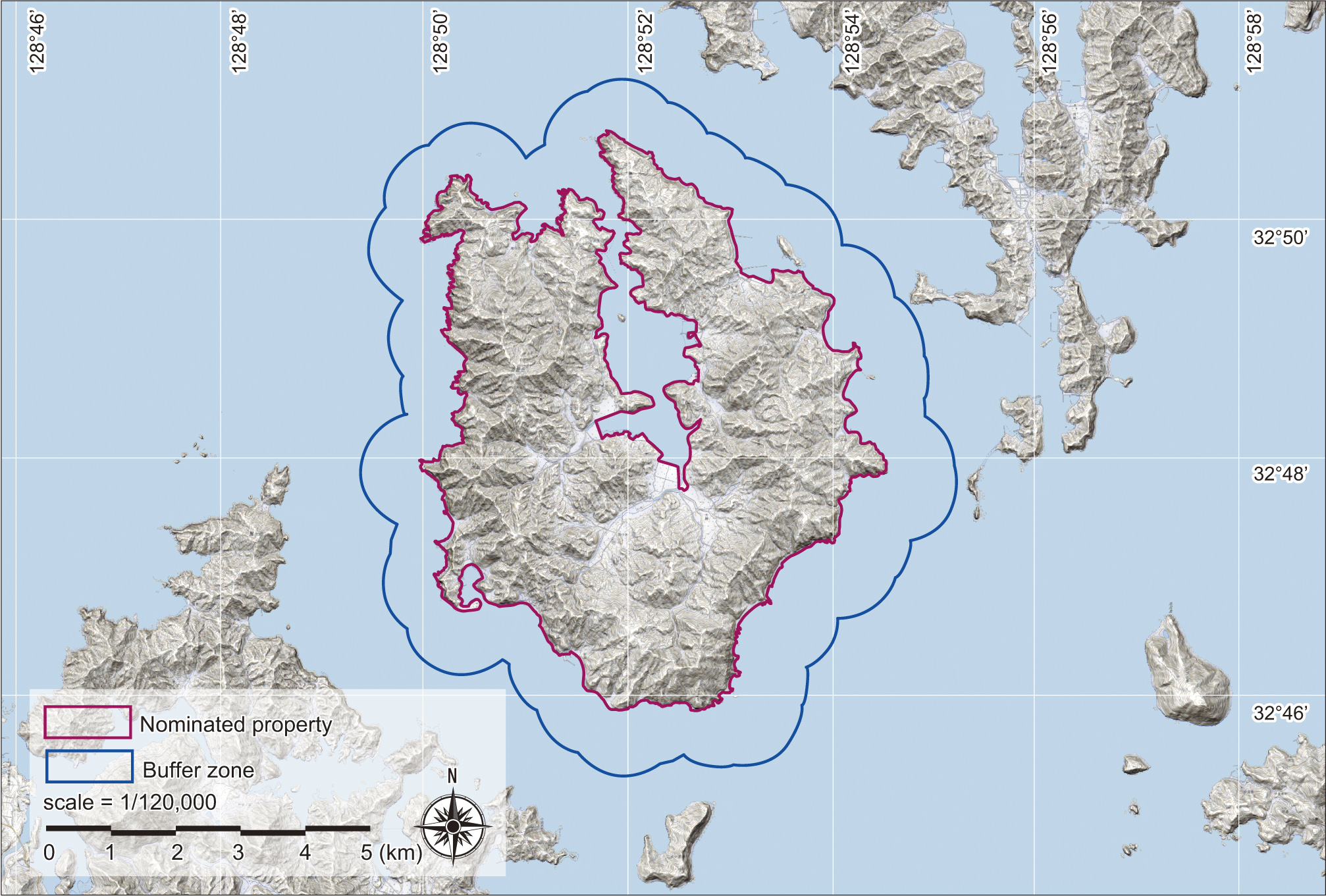
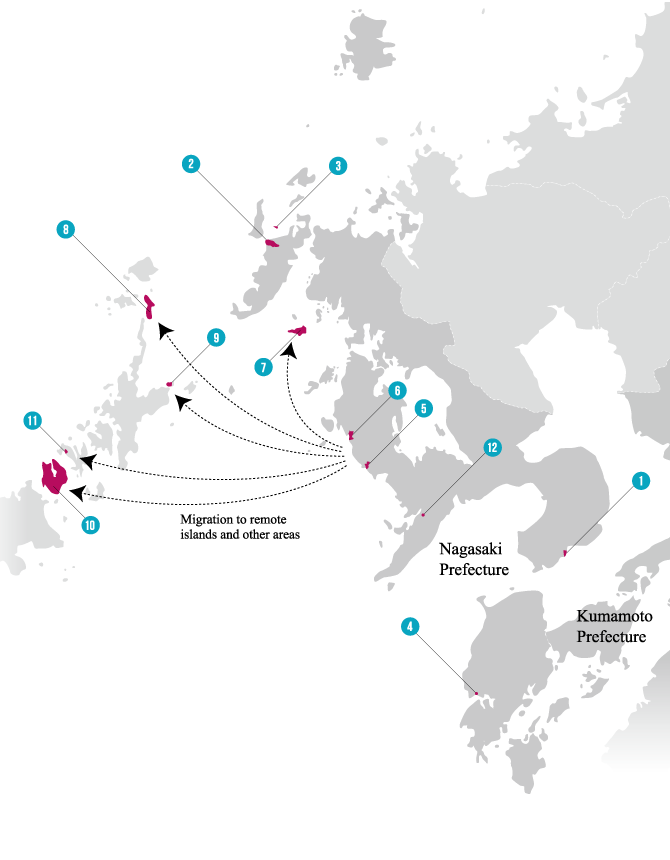
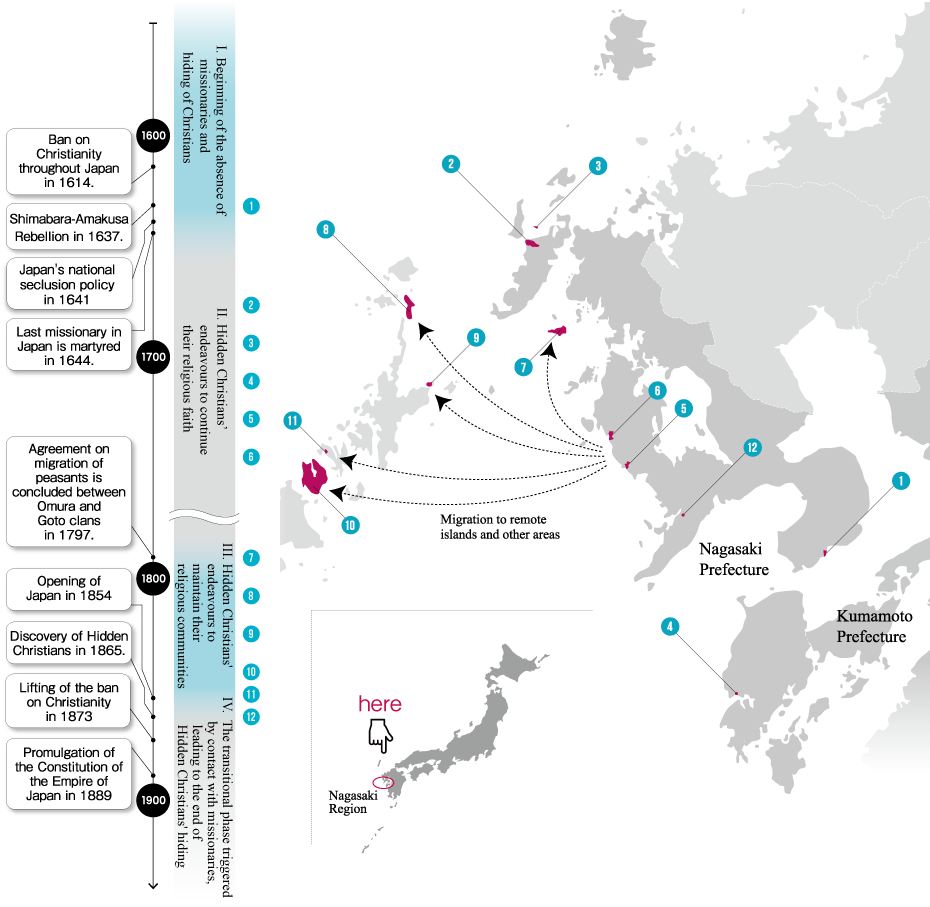
Hisaka Island is located in the southern part of the Goto Islands. This horseshoe-shaped island, with Hisaka Bay located in its centre, has a circumference of almost 52 km. This island still retains rice paddies that were once cultivated by the Hidden Christians who migrated there under an agreement between the feudal lords, the site of the Rokuroba where Hidden Christians collaborated with Buddhists in hauling in their fishing nets, Hidden Christian graveyards, places where persecution occurred after the Discovery of the Hidden Christians, the churches and their sites that were built after the lifting of the ban.
The first comprehensive Catholic mission in the Goto Islands was initiated by the Jesuit Luis de Almeida in 1566 on Fukue Island, located to the south of Hisaka Island. Although there is no direct record indicating missionary work being carried out on Hisaka Island, the names of Japanese Catholics are recorded in the early 17th century on Naru Island, which adjoins the north side of Hisaka. This suggests that it is highly likely that Christianity was also introduced to Hisaka Island, which is located between Fukue Island and Naru Island, in the late 16th or early 17th century.
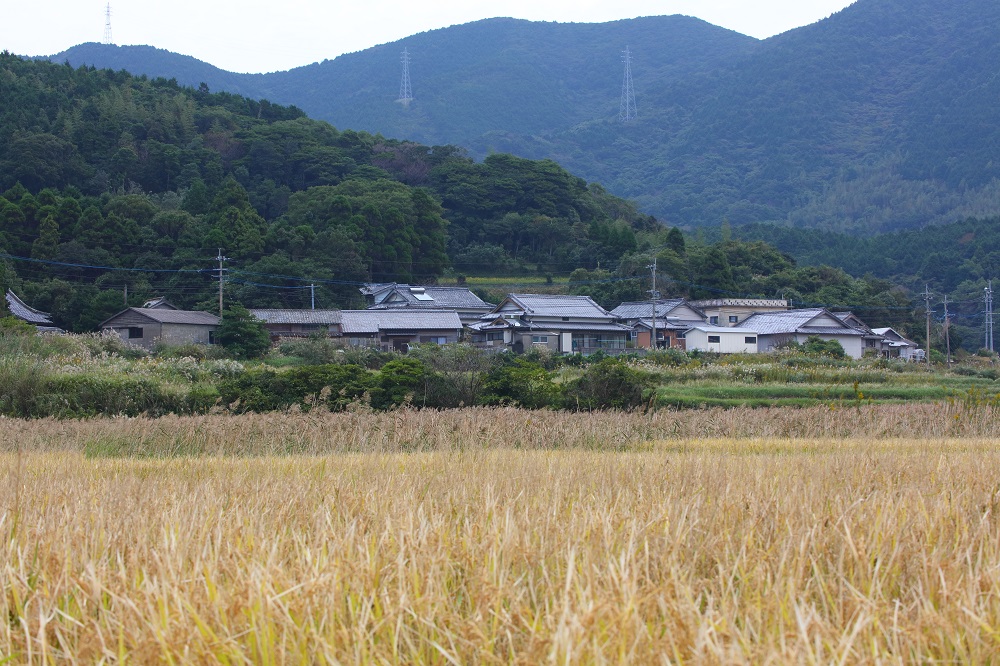
However, all the Japanese Catholics are thought to have disappeared from the Goto Islands by around the 18th century due to the comprehensive ban on Christianity imposed by the authorities. According to a document recording the situation of Hisaka Island in those days, 456 people lived on the island. This document also lists the names of then-existing villages such as Hisaka, Obiraki, Inoki, Ichikogi, and Warabi. These villages were built in areas of flat land suitable for cultivation. There were also fishing villages such as Tanoura, which served as the gateway to the island, and Fukaura, where the inhabitants were engaged in salt production. All of these villages were Buddhist communities under the control of the magistrate’s office which was stationed in Tanoura Village and later moved to Hisaka Village.
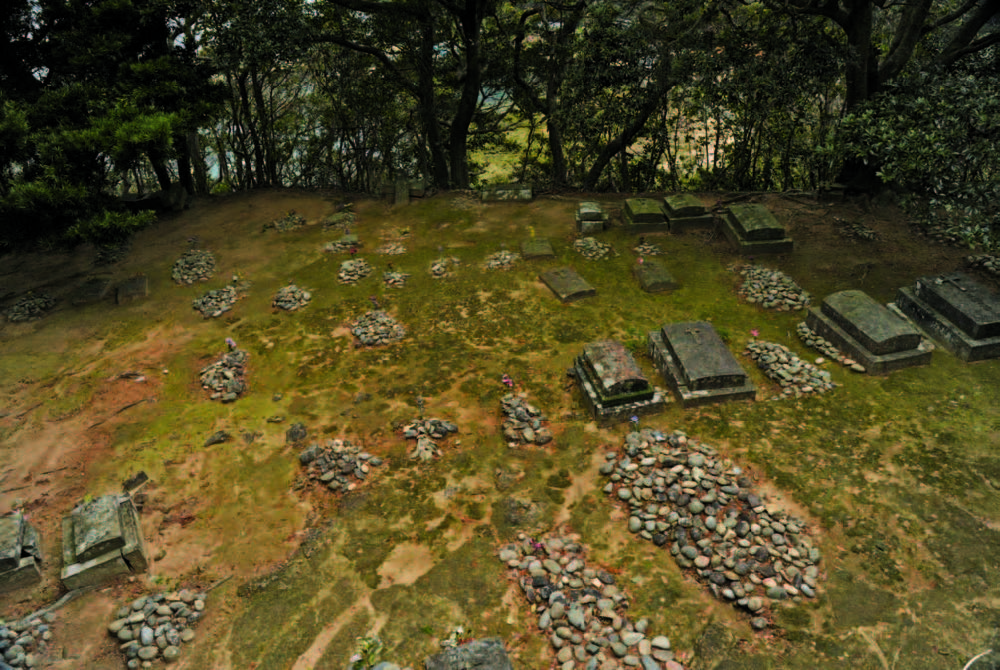
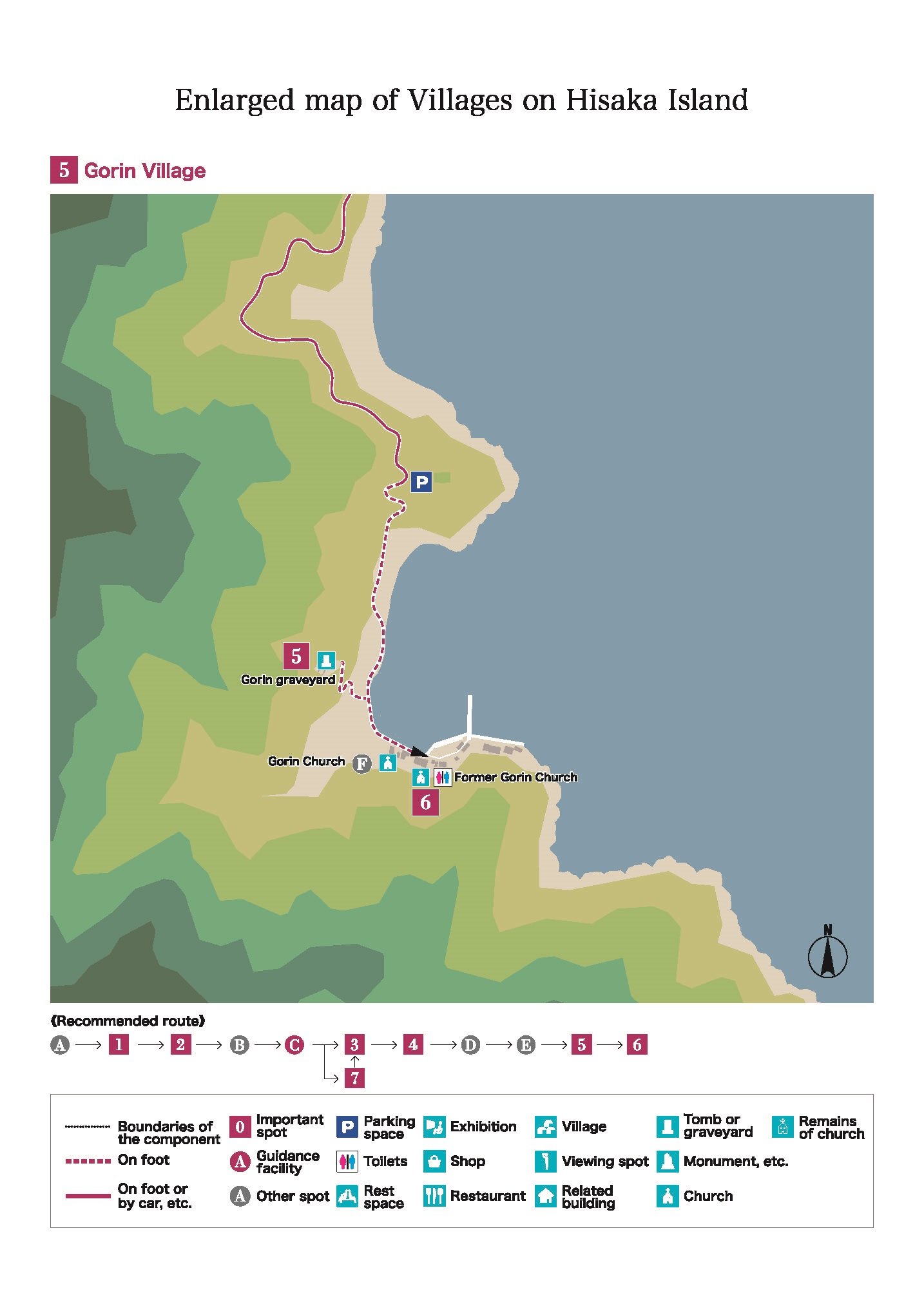
After the Omura and Goto clans had concluded an agreement on the migration of peasants from the Omura domain to the Goto domain in 1797, new villages were formed in the Goto Islands by the new arrivals collectively called Itsuki. Many of these were actually Hidden Christian villages. With the approval of the magistrate’s office, the migrants established their own villages on the periphery of pre-existing Buddhist villages (such as Eiri, Uchikamihira, and Sotokamihira) or in isolated places far from Buddhist villages (such as Gorin and Zazare). Hidden Christian graveyards still remain in Eiri, Zazare, Obiraki, Hamadomari and Gorin.
As these new communities had scarcely any land suitable for cultivation and since there were not enough people to open up new farmlands, the Hidden Christian migrants needed to build mutual cooperation with the existing Buddhist communities; for example, by developing new rice paddies next to those of the Buddhist communities, and by assisting in daily fishing and farming activities carried out by local Buddhists.
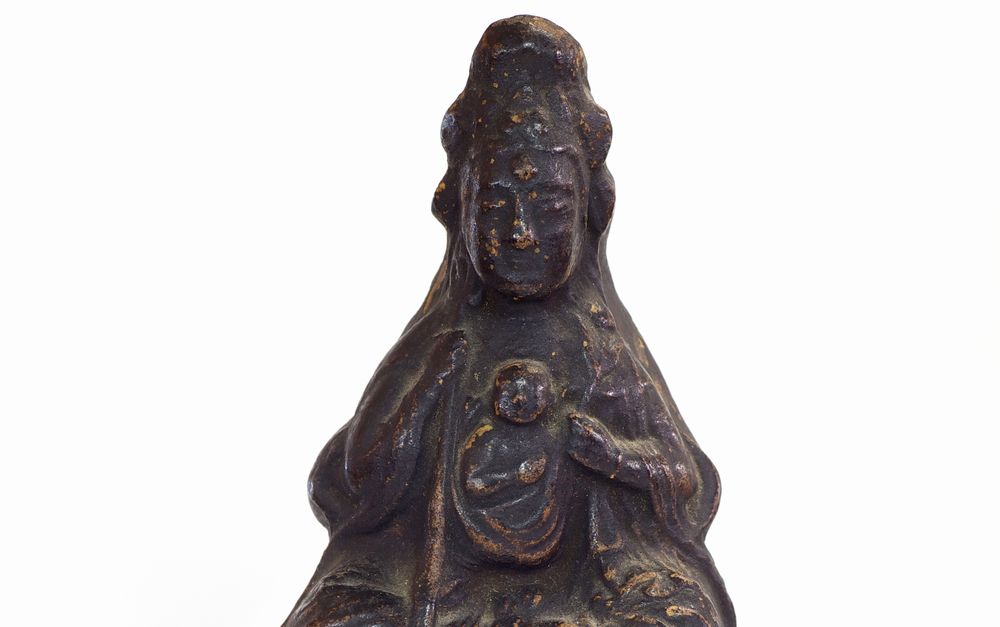
While the Hidden Christian migrants on Hisaka Island mutually cooperated with the pre-existing Buddhist communities, they secretly maintained their religious communities under their own leaders and continued practising their religion in each village. Hidden Christians of Eiri Village they secretly revered a white porcelain statue of Buddhist Bodhisattva Kannon brought from China as the Virgin Mary (Maria Kannon).
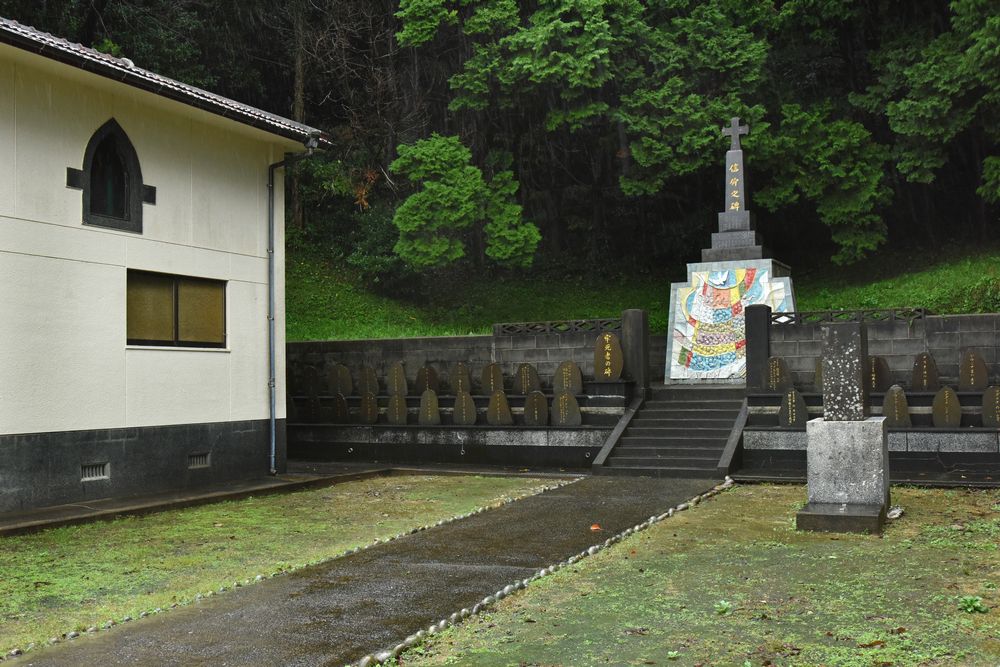
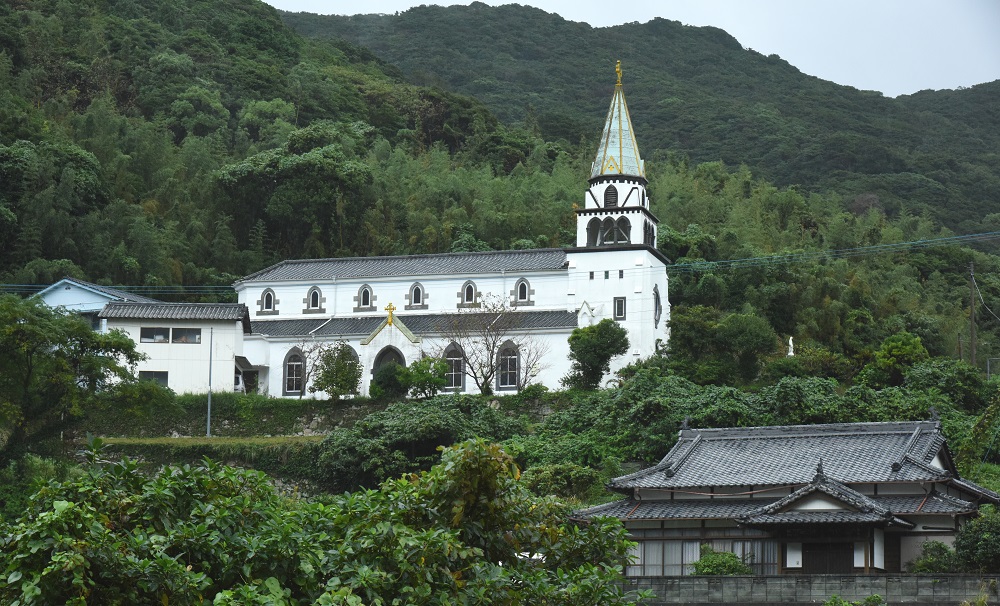
Following the Discovery of Hidden Christians at Oura Cathedral in 1865, Hidden Christian leaders in the communities scattered throughout the Nagasaki region secretly started contacting the European missionaries at the cathedral. Hidden Christians on Hisaka Island also contacted the missionaries to confess their faith and receive catechetical instruction. However, when the Hidden Christians on the island started revealing their faith in public, this resulted in a new wave of persecution (known as the Goto Kuzure) throughout the Goto Islands as the ban on Christianity had not been lifted yet. The authorities confined a large number of Hidden Christians in a small prison, and many lost their lives there (this incident is known as the ‘Royanosako Martyrdom’). Hisaka Island is known as the place where the final persecution of Hidden Christians occurred just before the lifting of the ban on Christianity in 1873. At the site of the martyrdom now stand a church and a memorial for the victims. For the Catholics on the island who joined the Catholic Church as their ancestors did in the 16th century, this site continues to hold great significance as a place of memory dating back to the period of the ban on Christianity.
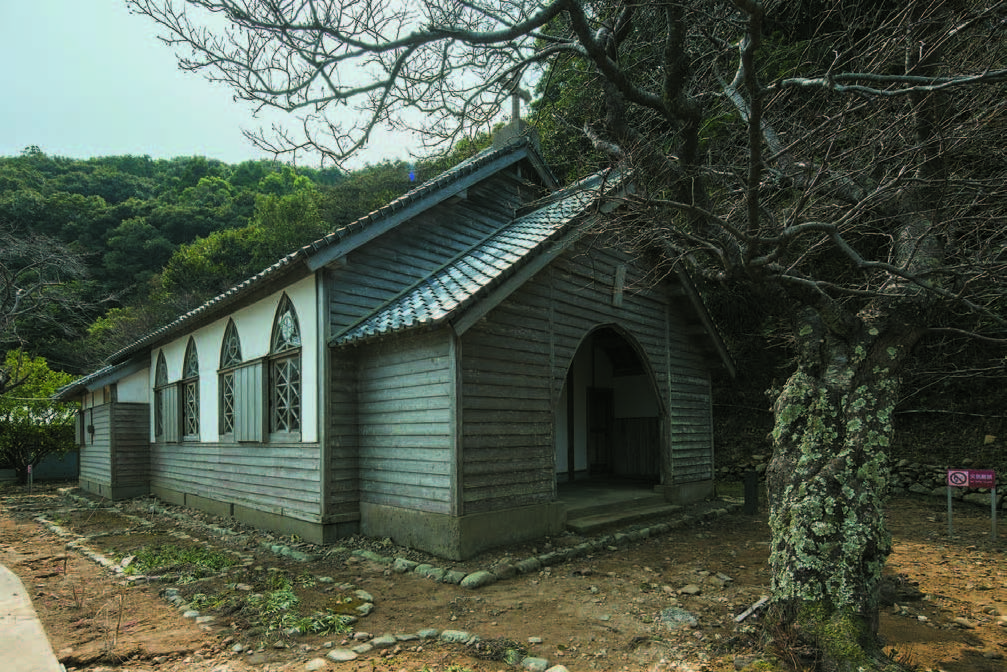
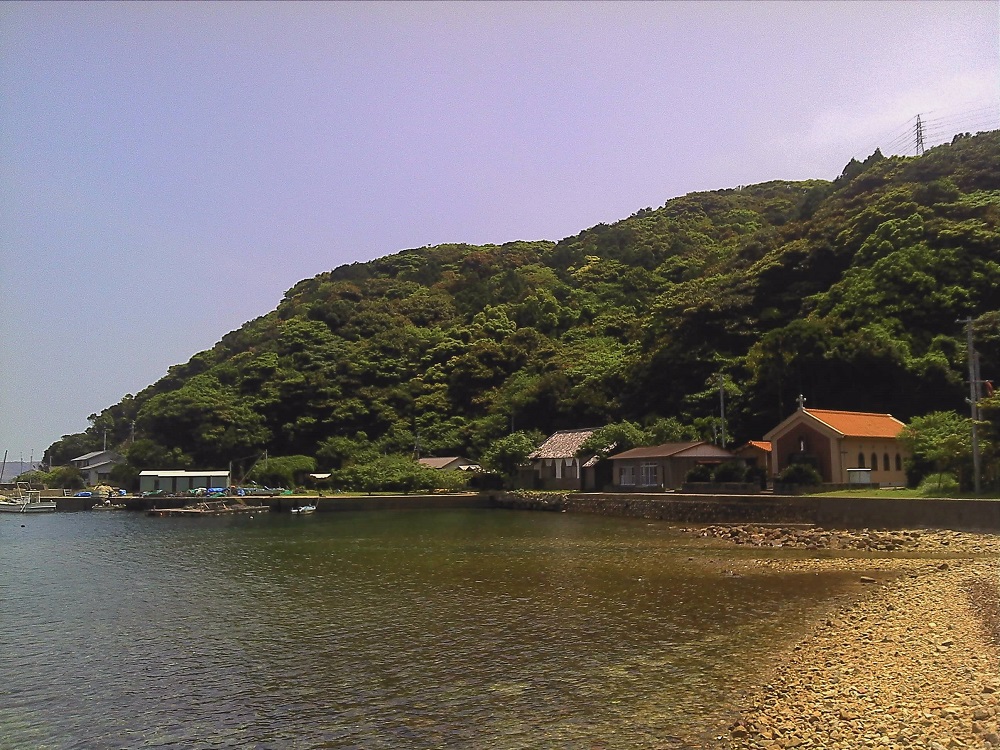
After the lifting of the ban, Hidden Christians on Hisaka Island rejoined the Catholic Church and churches were constructed in Hamawaki, Eiri, Zazare, and Akanita. These churches symbolically mark the end of Hidden Christians’ hiding on Hisaka Island. Hamawaki Church, the first on the island, was relocated to Gorin Village on the eastern coast, and it still exists today (the present Former Gorin Church).
 Villages on Hisaka Island
Villages on Hisaka Island
 (Ⅰ) Beginning of the absence of missionaries and hiding of Christians
(Ⅱ) Hidden Christians' endeavours to continue their religious faith
(Ⅲ) Hidden Christians' endeavours to maintain their religious communities
(Ⅳ) The transitional phase triggered by contact with missionaries, leading to the end of Hidden Christians' hiding
(Ⅰ) Beginning of the absence of missionaries and hiding of Christians
(Ⅱ) Hidden Christians' endeavours to continue their religious faith
(Ⅲ) Hidden Christians' endeavours to maintain their religious communities
(Ⅳ) The transitional phase triggered by contact with missionaries, leading to the end of Hidden Christians' hiding
















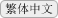
























 Remains of Hara Castle
Remains of Hara Castle Kasuga Village and Sacred Places in Hirado
Kasuga Village and Sacred Places in Hirado Kasuga Village and Sacred Places in Hirado
Kasuga Village and Sacred Places in Hirado Sakitsu Village in Amakusa
Sakitsu Village in Amakusa Shitsu Village in Sotome
Shitsu Village in Sotome Ono Village in Sotome
Ono Village in Sotome Villages on Kuroshima Island
Villages on Kuroshima Island Remains of Villages on Nozaki Island
Remains of Villages on Nozaki Island Villages on Kashiragashima Island
Villages on Kashiragashima Island Villages on Hisaka Island
Villages on Hisaka Island Egami Village on Naru Island
Egami Village on Naru Island Oura Cathedral
Oura Cathedral